The positivity over last Friday’s (3 May 2019) excellent US payrolls report, which showed robust job creation growth with no indication of wage pressure, proved short-lived!
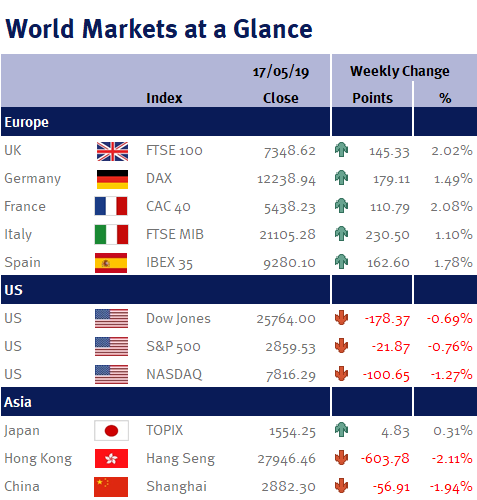
Week ending 10th May 2019.
13th May 2019
Two tweets from Donald Trump on Sunday (5 May 2019) caught everyone off guard and completely changed the financial market’s sentiment: seeking to increase pressure on China for more concessions, Donald Trump significantly increased tariffs on Chinese goods.
However, it is important not to panic. While the tweets have negatively impacted equity markets this week (as markets have focused on the worst possible outcome: a breakdown of talks and retaliatory tariffs), it is important to note that talks are continuing. In fact, China’s chief trade negotiator, Vice Premier Liu He, travelled to the US for further talks yesterday and today (9 & 10 May 2019), signalling their willingness to continue talking and eventually reach an agreement.
Also, experience of the past year or so, shows that equities can still push higher – especially as Donald Trump’s tweets often don’t pan-out as he writes or implies. And while higher tariffs could result in higher CPI inflation, it is highly likely that the major central banks will maintain their dovish tilt to support economic growth, which should be positive for equity markets.
Furthermore, Donald Trump’s aim was obviously to try and shake-up talks in order to speed-up negotiations rather than kill any trade deal, suggesting that the equity market sell-off may be short-lived.
Additionally, data from China this week suggests that it is in their interests to continue working towards an agreement rather than calling Donald Trump’s bluff, as data shows that China’s exports dropped in April by 2.7% (reducing its monthly trade surplus to $13.84bn from $32.64bn), while the IMF believes that China’s economy will be reduced by 1.5% in an all-out-trade-war with the US.
Unfortunately, the renewal of US/China trade tensions overshadowed this week’s economic data.
Both core and headline US CPI inflation for April picked up by 0.1% to 2.1% and 2.0% respectively. While this will provide some ammunition for the Fed Chairman, Jay Powell’s claim that the recent slowdown in inflation is only temporary, it should be noted that US PPI (producer price inflation) rose by less than expected in April. Excluding food and energy, producer prices increased by 2.4% compared to a year earlier – and as this data measures wholesale and other selling costs at businesses, it suggests that inflationary pressures coming through the pipeline for consumers (CPI inflation) are likely to remain elusive.
Elsewhere, the UK economy grew by 0.5% in the first quarter, picking up from 0.2% during Q4 2018. However, this was mainly due to companies building up stock levels ahead of the original Brexit date of 29 March 2019, as this added 0.7% to growth during the quarter. Rolling month-on-month GDP shows that the economy actually shrank by 0.1% in March – suggesting growth will slow during Q2 2019 as stockpiling unwinds. Additionally, many companies such as BMW’s Mini and Peugeot’s Vauxhall car factories went ahead with their planned Brexit disruption related shutdowns in April, which will also impact Q2 GDP data.
Looking ahead to next week, in the UK we have employment data (unemployment rate and weekly earnings); US retail sales; the University of Michigan Consumer Sentiment Index; Eurozone CPI; Eurozone Q1 GDP; and Chinese retail sales.
Investment Management Team
The latest market updates are brought to you by Investment Managers & Analysts at Wealth at Work Limited which is a member of the Wealth at Work group of companies.
Links to websites external to those of Wealth at Work Limited (also referred to here as 'we', 'us', 'our' 'ours') will usually contain some content that is not written by us and over which we have no authority and which we do not endorse. Any hyperlinks or references to third party websites are provided for your convenience only. Therefore please be aware that we do not accept responsibility for the content of any third party site(s) except content that is specifically attributed to us or our employees and where we are the authors of such content. Further, we accept no responsibility for any malicious codes (or their consequences) of external sites. Nor do we endorse any organisation or publication to which we link and make no representations about them.

